Magellanic System in OGLE-IV
OGLE-ing the Magellanic System: 3-D Structure of the Clouds and the Bridge using RR Lyrae Stars
S. Kozłowski, Ł. Wyrzykowski, M. Pawlak, M. K. Szymański, K. Ulaczyk
2016, arXiv:1611.02709
We present a 3-D analysis of a sample of 22 859 type ab RR Lyrae stars in the Magellanic System from the OGLE-IV Collection of RR Lyrae stars. The distance to each object was calculated based on its photometric metallicity and a theoretical relation between color, absolute magnitude and metallicity.
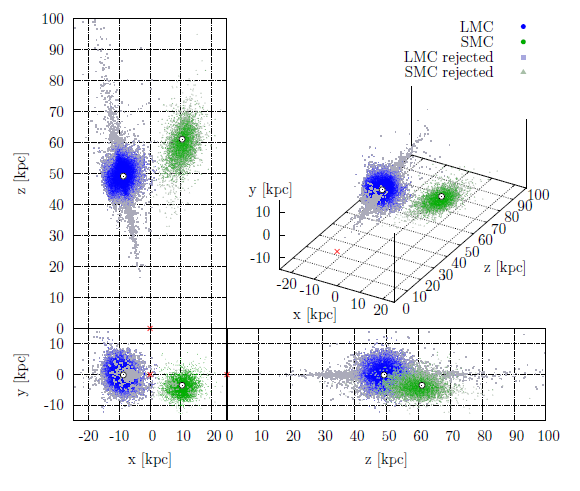
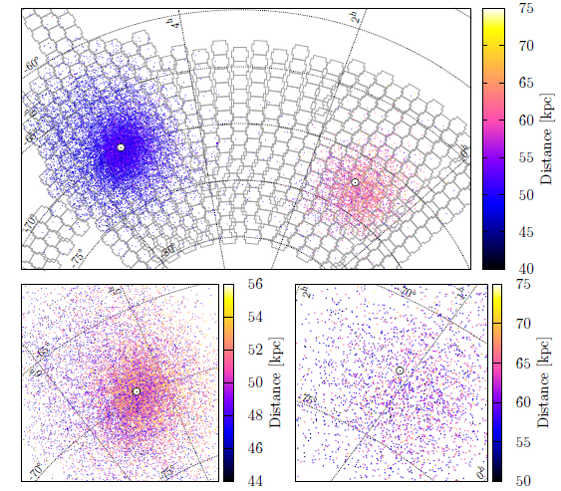
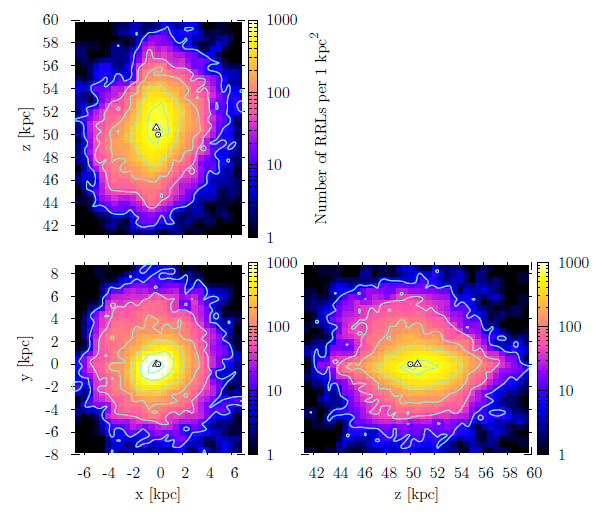
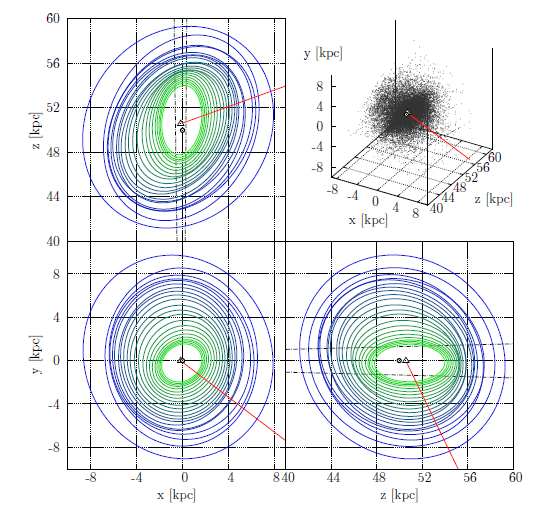
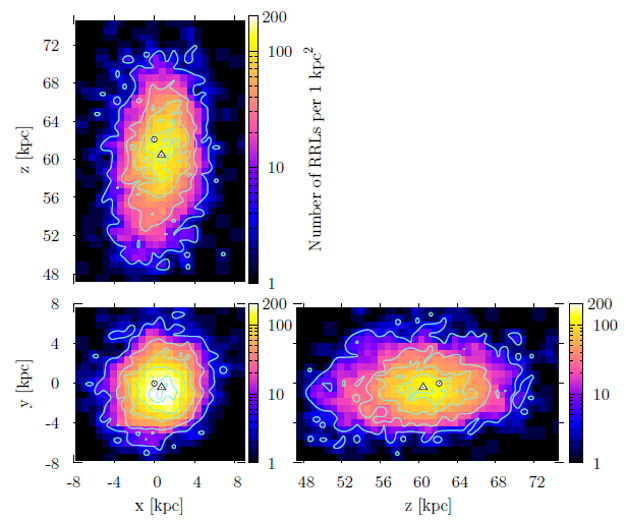
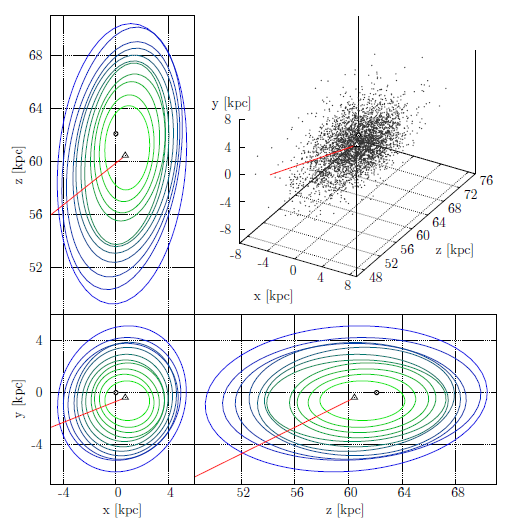
The LMC RR Lyrae distribution is very regular and does not show any substructures. We demonstrate that the bar found in previous studies may be an overdensity caused by blending and crowding effects. The halo is asymmetrical with a higher stellar density in its north-eastern area, which is also located closer to us. Triaxial ellipsoids were fitted to surfaces of a constant number density. Ellipsoids farther from the LMC center are less elongated and slightly rotated toward the SMC. The inclination and position angle change significantly with the a axis size. The median axis ratio is 1:1.23:1.45.
The RR Lyrae distribution in the SMC has a very regular, ellipsoidal shape and does not show any substructures or asymmetries. All triaxial ellipsoids fitted to surfaces of a constant number density have virtually the same shape (axis ratio) and are elongated along the line of sight. The median axis ratio is 1:1.10:2.13. The inclination angle is very small and thus the position angle is not well defined.
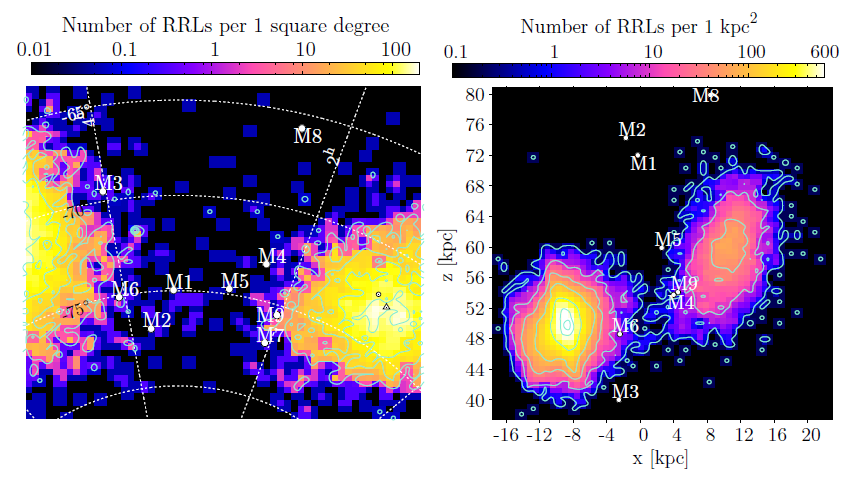
We present the distribution of RR Lyrae stars in the Magellanic Bridge area, showing that the Magellanic Clouds' halos overlap. A comparison of the distributions of RR Lyrae stars and Classical Cepheids shows that the former are significantly more spread and distributed regularly, while the latter are very clumped and form several distinct substructures.
Computer readable Table 2 from the Paper is available for download here: table2.dat
| Location | OCVS_Id | P | I | V | WI,V-I | [Fe/H] | R.A. | Dec | d | x | y | z | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [d] | [mag] | [mag] | [mag] | [dex] | [h] | [deg] | [kpc] | [kpc] | [kpc] | [kpc] | |||||||
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00001 | 0.6347521 | 18.772 | 19.455 | 17.713 | -1.63 | 0.12 | 04:27:45.45 | -70:43:12.0 | 50.23 | 1.46 | -4.83 | 0.39 | 0.44 | 0.85 | 49.99 | 1.54 |
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00003 | 0.6564971 | 18.649 | 19.306 | 17.631 | -1.41 | 0.11 | 04:28:08.50 | -70:21:22.8 | 48.44 | 1.39 | -4.77 | 0.38 | 0.71 | 0.82 | 48.20 | 1.48 |
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00005 | 0.6433519 | 18.942 | 19.613 | 17.902 | -1.14 | 0.42 | 04:28:21.06 | -70:08:54.5 | 53.33 | 2.13 | -5.32 | 0.45 | 0.96 | 0.90 | 53.06 | 2.19 |
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00006 | 0.6000192 | 18.766 | 19.458 | 17.693 | -1.42 | 0.09 | 04:28:28.18 | -70:41:44.4 | 47.69 | 1.36 | -4.64 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.80 | 47.46 | 1.44 |
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00008 | 0.7877152 | 18.674 | 19.394 | 17.558 | -0.90 | 0.23 | 04:28:57.78 | -70:17:16.6 | 49.62 | 1.59 | -4.96 | 0.40 | 0.77 | 0.84 | 49.37 | 1.66 |
| LMC | OGLE-LMC-RRLYR-00010 | 0.5940743 | 18.813 | 19.472 | 17.791 | -1.26 | 0.12 | 04:29:19.47 | -70:41:24.1 | 49.12 | 1.42 | -4.84 | 0.39 | 0.42 | 0.83 | 48.88 | 1.51 |
| see whole Table | |||||||||||||||||
- [Fe/H] - photometric metallicity on the Jurcsik (1995) scale
- d - distance from the observer
- x,y,z - the cartesian coordinates
PLEASE cite the following paper when using the data or referring to these OGLE results:
Jacyszyn-Dobrzeniecka et al., 2017, Acta Astronomica, 67, 1, arXiv:1611.02709
Any comments about the data and the form of their presentation are welcome as they can improve the future releases of OGLE analysis. Send your messages to this address.
 back
back